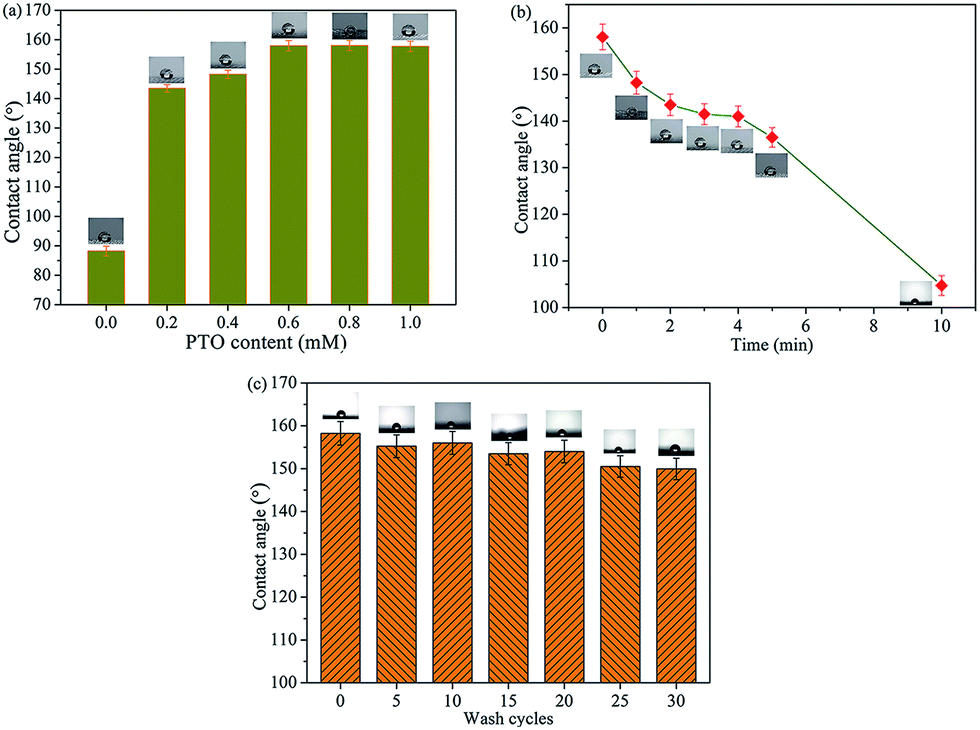
Robust superhydrophobic and self-lubricating PTES-TiO 2 @UHMWPE fabric and its tribological properties - RSC Advances (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/C6RA28255E

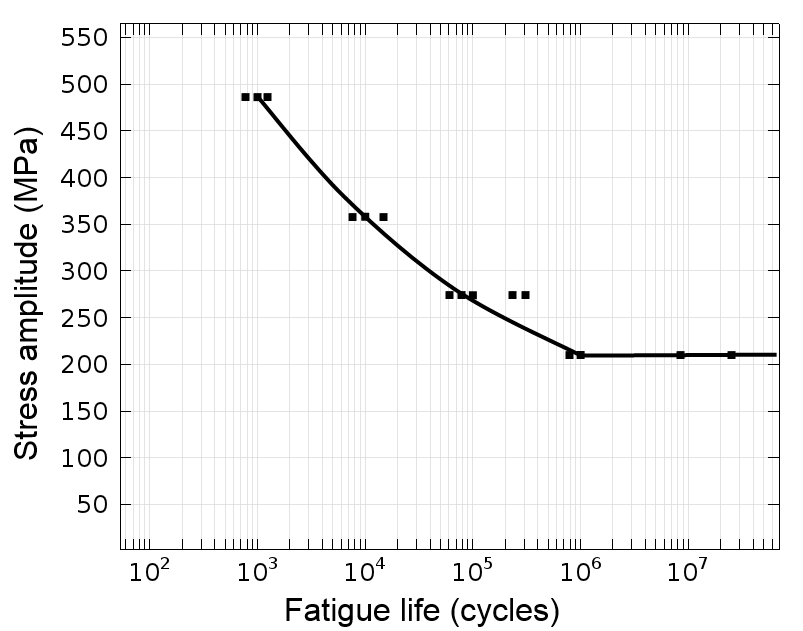
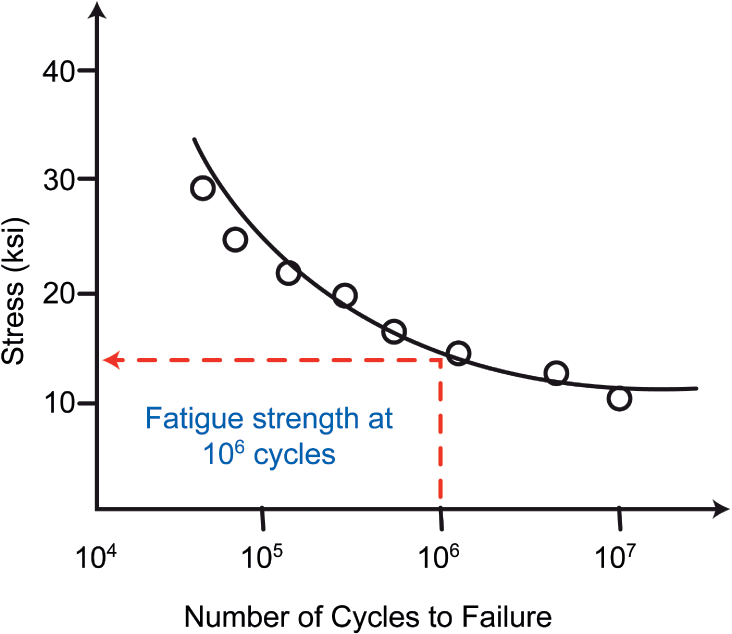
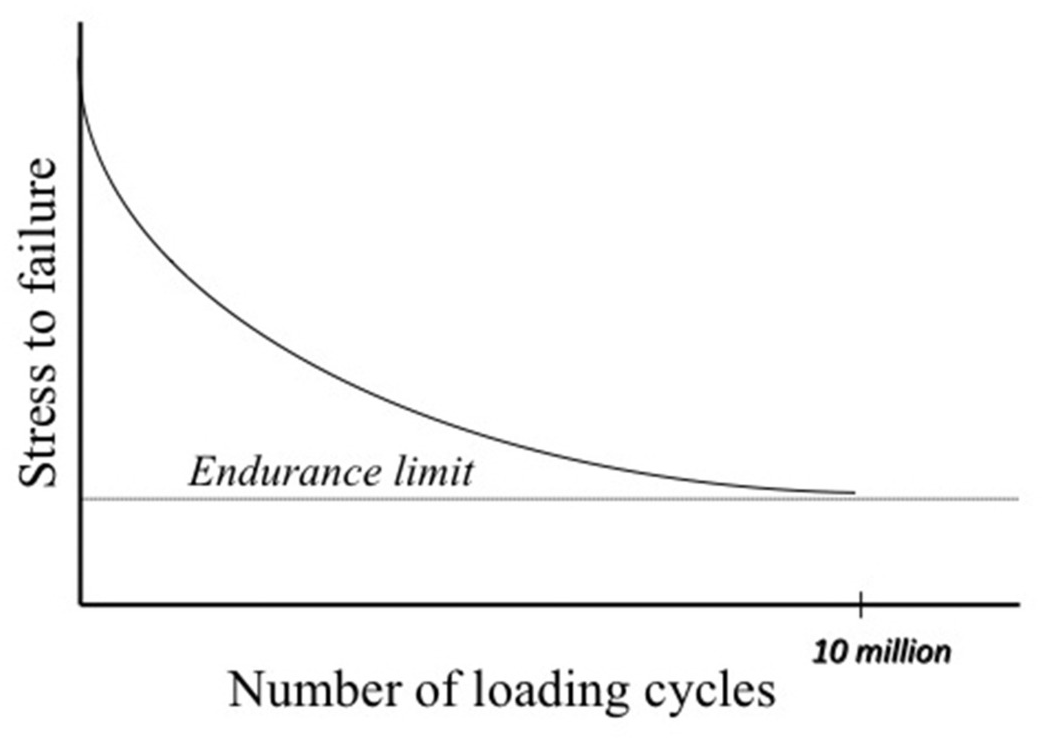
Mechanical fatigue of polymers: A new approach to characterize the SN behavior on the basis of macroscopic crack growth mechanism - ScienceDirect

Wear Behaviour and Wear Debris Characterization of UHMWPE on Alumina Ceramic, Stainless Steel, CoCrMo and Ti6Al4V Hip Prostheses in a Hip Joint Simulator | Scientific.Net

Fatigue characteristics of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene with different molecular weight for implant material | Request PDF
The Interplay of Design and Materials in Orthopedics: Evaluating the Impact of Notch Geometry on Fatigue Failure of UHMWPE Joint